the intestinal permeability ip assessment is a noninvasive test procedure|Fecal and Circulating Biomarkers for the Non : service The Intestinal Permeability (IP) test, also referred to as a “leaky gut” test, is a precise and non-invasive method for assessing gastrointestinal mucosal integrity. Damage to the lining of the .
WEBmail biopse.com.br Acesse e gerencie seu e-mail de qualquer lugar e conte com diversos recursos. ACESSAR WEBMAIL. Conecte-se utilizando o sistema de webmail Roundcube . Email: @biopse.com.br . Senha: Esqueceu a senha? .
{plog:ftitle_list}
18 de jun. de 2017 · Um cara da plateia decidiu ficar noivo no meio do meu show e eu dei um jeito desse pedido ficar especial, mas do meu jeito
The noninvasive assessment of intestinal permeability in humans has a 20-year history. Because the tests are increasingly used in clinical practice and research and because there is much controversy, we reviewed the literature and outlined the potential and possible shortcomings of .The lactulose and mannitol ratio is a useful, simple, non-invasive and a reliable test .The noninvasive assessment of intestinal permeability in humans has a 20-year history. Because the tests are increasingly used in clinical practice and research and because there is much .
custom ge surveymaster protimeter moisture meter manual
Intestinal Permeability Assessment Interpretation Guide. There are two primary methods used clinically to assess leaky gut: the lactulose/mannitol permeability assay (through Genova, .The noninvasive assessment of intestinal permeability in humans has a 20-year history. Because the tests are increasingly used in clinical practice and research and because there is much .
The Intestinal Permeability (IP) test, also referred to as a “leaky gut” test, is a precise and non-invasive method for assessing gastrointestinal mucosal integrity. Damage to the lining of the . In this approach, participants drink an oral dose of a fluorescent dye (fluorescein) and a fibre-optic fluorescence spectrometer is attached to the finger to detect permeation of . This study reveals the potential of transcutaneous fluorescence spectroscopy for non-invasive assessment of intestinal permeability. Our results demonstrate the ability of .
Intestinal permeability is getting more and more attention in gastrointestinal research. Although well recognized, its exact role in health and disease is yet to be defined. The lactulose and mannitol ratio is a useful, simple, non-invasive and a reliable test for estimation of intestinal permeability. 13 In this test, while mannitol uses smaller and .
Moreover, a study aiming to validate six potential biomarkers of intestinal permeability (albumin, calprotectin, and zonulin measured in feces, as well as intestinal fatty .The basis of non-invasive tests that could be used for clinical assessment of intestinal permeability came from observations in patients with coeliac disease, initially suspected of having increased intestinal permeability because of disacchariduria [25, 261. At the same time there was growing interest in the mode intestinal'Leaky gut' has been found in intestinal and extra-intestinal diseases. However, functional evaluation of intestinal permeability is not widely used as a diagnostic marker, possibly owing to significant limitations of currently used permeability assays. There is an unmet need for development of a new, non-invasive test to assess intestinal . Keywords: intestinal barrier; non-invasive biomarkers; intestinal permeability; tight junctions 1. Introduction The concept of the “leaky gut”, also known as increased intestinal permeability (IP), and its association with the development and progression of a .
The Small Intestinal Bacteria Overgrowth (SIBO) profiles are non-invasive breath tests which capture exhaled hydrogen (H2) and methane (CH4) . Intestinal Permeability Assessment #2305 | Sample Report | Instructions. Microbiology Analysis #2300 . Looking to order a test for yourself? With Genova Connect, you can easily order gut health . The permeability of the intestinal barrier is altered in a multitude of gastrointestinal conditions such as Crohn's and coeliac disease. However, the clinical utility of gut permeability is currently limited due to a lack of reliable diagnostic tests. To address this issue, we report a novel techniq .
This content was downloaded from IP address 162.43.237.108 on 27/10/2022 at 20:46 . Intestinal permeability is a functional feature of the . transcutaneous fluorescence spectroscopy for non .
1. Introduction. The concept of the “leaky gut”, also known as increased intestinal permeability (IP), and its association with the development and progression of a plethora of gastrointestinal disorders, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome, as well as other diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, asthma, and .Objective: To assess the effectiveness of the combined use of fecal calprotectin (FC), anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody (ASCA), perinuclear staining antineutrophil antibody (pANCA), small intestinal permeability test (IP), and bowel wall ultrasonography measurement (BWUS) in the diagnostic work-up of children with suspected inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The study of intestinal permeability is gaining growing interest due to its relevance in the onset and progression of several gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal diseases. Though the involvement of impaired intestinal permeability in the pathophysiology of such diseases is recognized, there is .
Background A widely used method in assessing small bowel permeability is the lactulose:mannitol test, where the lactulose:mannitol ratio (LMR) is measured. However, there is discrepancy in how the test is conducted and in the values of LMR obtained across studies. This meta-analysis aims to determine LMR in healthy subjects, coeliac and Crohn’s disease. . Transcutaneous fluorescence spectroscopy shows promise in non-invasively discriminating between two differing states of gut permeability, demonstrating potential for future clinical use. The permeability of the intestinal barrier is altered in a multitude of gastrointestinal conditions such as Crohn’s and coeliac disease. However, the clinical utility of gut . Intestinal permeability is an important diagnostic marker, yet its determination by established tests, which measure the urinary excretion of orally administered tracer molecules, is time consuming and can only be performed prospectively. . Biomarkers for assessment of intestinal permeability in clinical practice Am J Physiol Gastrointest .
The non-invasive evaluation of intestinal permeability (IP) and the assessment of intestinal inflammation 123 Biometals through the measurement of fecal lactoferrin (FL) were proposed for the diagnostic work-up of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms (Ford et al. 1985; Tibble et al. 2002; Schoepfer et al. 2008) and chronic diarrhea (Di Leo .A major task of the intestine is to form a defensive barrier to prevent absorption of damaging substances from the external environment. This protective function of the intestinal mucosa is called permeability. Clinicians can use inert, nonmetabolized sugars such as mannitol, rhamnose, or lactulose to measure the permeability barrier or the degree of leakiness of the . The sugar-based intestinal permeability test is a simple, non-invasive procedure that enables us to reliably assess intestinal barrier alterations. The performance of this protocol allows satisfactory assessment of intestinal permeability, nevertheless it is not validated, and further studies are needed.
The study of intestinal permeability is gaining growing interest due to its relevance in the onset and progression of several gastrointestinal and non-gastrointestinal diseases. Though the involvement of impaired intestinal .
Intestinal Permeability (IP) The Intestinal Permeability (IP) test, also referred to as a “leaky gut” test, is a precise and non-invasive method for assessing gastrointestinal mucosal integrity. Damage to the lining of the gastrointestinal tract (small and large intestine) is common in people with conditions such as food sensitivity and food The lactulose/mannitol (L/M) intestinal permeability test is a simple, non-invasive screening test for coeliac disease. The reliability of the L/M test has so far only been tested in selected .
A major asset in experimental models is a reliable test that is able to measure the gut integrity of the birds. The evaluation of the IP in broilers is particularly performed using molecules or .The incorporation of noninvasive diagnostic tests into the initial diagnostic approach may avoid unnecessary invasive procedures and facilitate clinical decision-making when the diagnosis of IBD in children is initially uncertain. . perinuclear staining antineutrophil antibody (pANCA), small intestinal permeability test (IP), and bowel wall . Though the involvement of impaired intestinal permeability in the pathophysiology of such diseases is recognized, there is currently a need to identify non-invasive biomarkers or tools that are . Intestinal permeability is a functional feature of the intestinal wall that defines the degree to which molecules can pass from the intestine into the blood stream at given sites [].Two aspects of gut permeability that can be measured are transcellular permeability (representing passage through the water pores of cell membranes) and paracellular .
1 INTRODUCTION. The gut–blood barrier (GBB) is a complex system that protects an organism against the external environment. Intestinal wall integrity and the proper functioning of the GBB depend on the interaction of the circulatory system, immunological system, hormonal system and other factors (Farhadi, Banan, Fields, & Keshavarzian, 2003).An increased GBB . Non-invasive markers able to identify patients with chronic diarrhea at risk of organic disease are missing. Aim of the study was to assess the diagnostic ability of intestinal permeability (IP) test and fecal lactoferrin (FL) in distinguishing functional from organic disease in patients with chronic diarrhea. We retrospectively enrolled patients referring to the . The FD-4 intestinal permeability test was dose-dependent as we found a significant increase in plasma levels of FD-4 in obese mice with the bodyweight dose regimen. . Ostaff MJ, Wehkamp J .
Moreover, the allergic group showed a lactulose/mannitol ratio that was significantly different (0.105 +/- 0.071, p < 0.001). The intestinal permeability test for the diagnosis of food allergies seems to be a sensitive and non-invasive test that is well suited to the paediatric practice. The molecular components of differing sizes cross the intestinal epithelium at different rates, and PEG probes are suggested to be particularly suitable markers for the whole gut permeability assessment in a broad range of intestinal diseases, although both decreased and increased IP have been found [85–89]. This discrepancy could be due to .
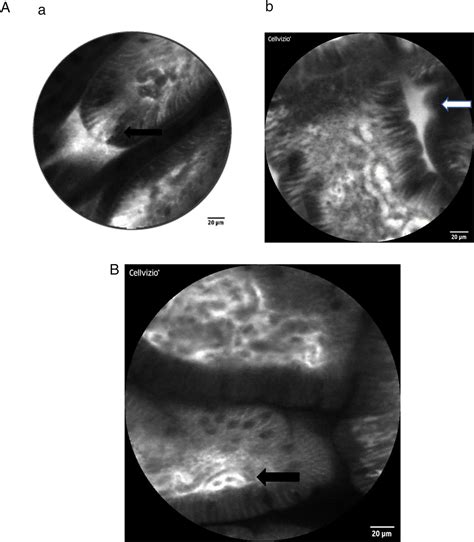
Visualising and quantifying intestinal permeability
WEB5 de ago. de 2020 · Empire Earth IV v9.8.0 (English) Download: EE4 9.8.0 + 1.5 English. Version with support for the 1.5 patch Dr. MonaLisa with all the bonuses that the patch gives. The main thing is fewer problems with new ones. operating systems and the ability to play multiplayer on Dr.MonaLisa servers.
the intestinal permeability ip assessment is a noninvasive test procedure|Fecal and Circulating Biomarkers for the Non